ES简介
ES(Elasticsearch)是一个分布式全文搜索引擎,重点是全文搜索。
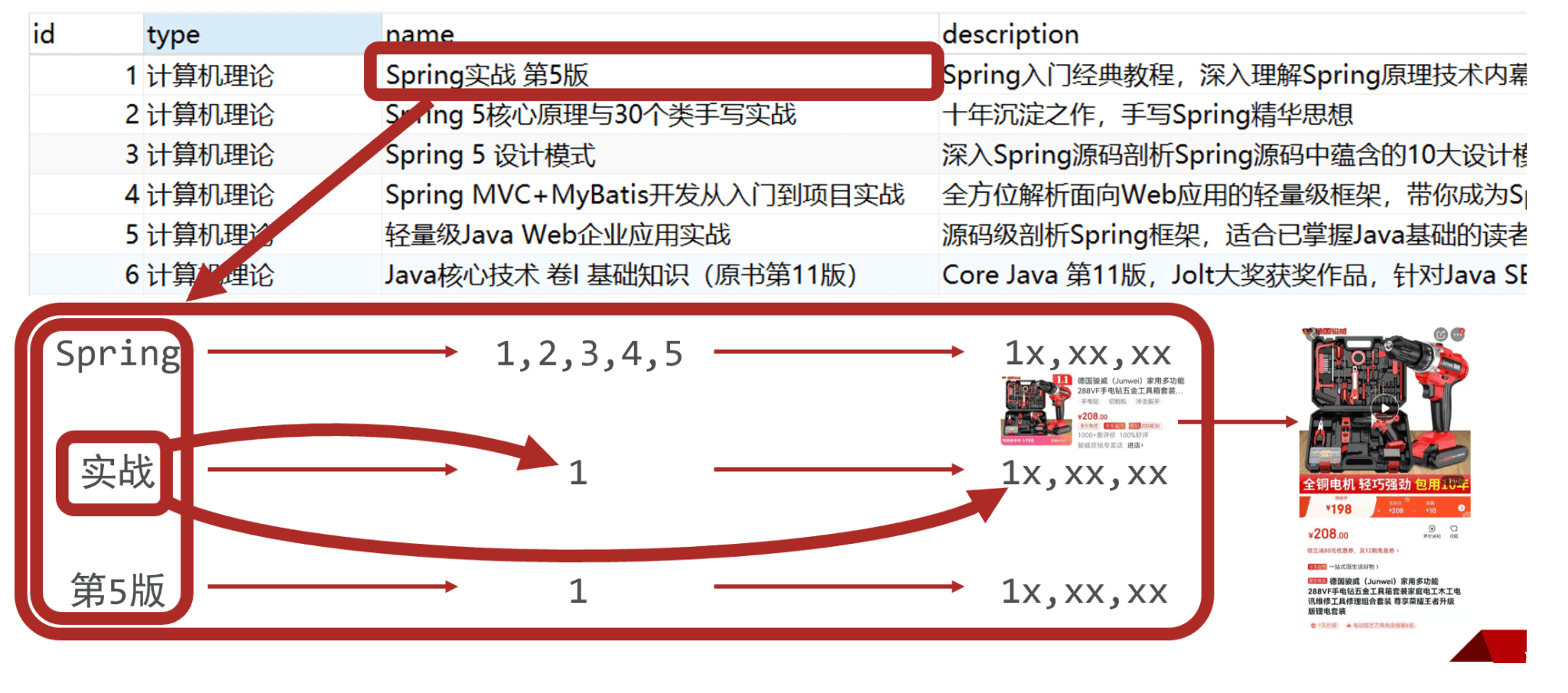
那什么是全文搜索呢?比如用户要买一本书,以Java为关键字进行搜索,不管是书名中还是书的介绍中,甚至是书的作者名字,只要包含java就作为查询结果返回给用户查看,上述过程就使用了全文搜索技术。搜索的条件不再是仅用于对某一个字段进行比对,而是在一条数据中使用搜索条件去比对更多的字段,只要能匹配上就列入查询结果,这就是全文搜索的目的。而ES技术就是一种可以实现上述效果的技术。
要实现全文搜索的效果,不可能使用数据库中like操作去进行比对,这种效率太低了。ES设计了一种全新的思想,来实现全文搜索。具体操作过程如下:
将被查询的字段的数据全部文本信息进行查分,分成若干个词
- 例如“中华人民共和国”就会被拆分成三个词,分别是“中华”、“人民”、“共和国”,此过程有专业术语叫做分词。分词的策略不同,分出的效果不一样,不同的分词策略称为分词器。
将分词得到的结果存储起来,对应每条数据的id
例如id为1的数据中名称这一项的值是“中华人民共和国”,那么分词结束后,就会出现“中华”对应id为1,“人民”对应id为1,“共和国”对应id为1
例如id为2的数据中名称这一项的值是“人民代表大会“,那么分词结束后,就会出现“人民”对应id为2,“代表”对应id为2,“大会”对应id为2
此时就会出现如下对应结果,按照上述形式可以对所有文档进行分词。需要注意分词的过程不是仅对一个字段进行,而是对每一个参与查询的字段都执行,最终结果汇总到一个表格中
| 分词结果关键字 |
对应id |
| 中华 |
1 |
| 人民 |
1,2 |
| 共和国 |
1 |
| 代表 |
2 |
| 大会 |
2 |
当进行查询时,如果输入“人民”作为查询条件,可以通过上述表格数据进行比对,得到id值1,2,然后根据id值就可以得到查询的结果数据了。(倒排索引)
ES下载与安装
windows版安装包下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/elasticsearch
下载的安装包是解压缩就能使用的zip文件,解压缩完毕后会得到如下文件
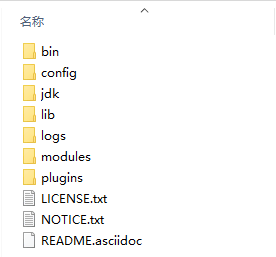
- bin目录:包含所有的可执行命令
- config目录:包含ES服务器使用的配置文件
- jdk目录:此目录中包含了一个完整的jdk工具包,版本17,当ES升级时,使用最新版本的jdk确保不会出现版本支持性不足的问题
- lib目录:包含ES运行的依赖jar文件
- logs目录:包含ES运行后产生的所有日志文件
- modules目录:包含ES软件中所有的功能模块,也是一个一个的jar包。和jar目录不同,jar目录是ES运行期间依赖的jar包,modules是ES软件自己的功能jar包
- plugins目录:包含ES软件安装的插件,默认为空
启动服务器
双击elasticsearch.bat文件即可启动ES服务器,默认服务端口9200。通过浏览器访问http://localhost:9200 看到如下信息视为ES服务器正常启动
{
"name" : "CZBK-**********",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "j137DSswTPG8U4Yb-0T1Mg",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.16.2",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "zip",
"build_hash" : "2b937c44140b6559905130a8650c64dbd0879cfb",
"build_date" : "2021-12-18T19:42:46.604893745Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.10.1",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
|
ES索引操作
ES中保存有我们要查询的数据,只不过格式和数据库存储数据格式不同而已。在ES中我们要先创建倒排索引,这个索引的功能又点类似于数据库的表,然后将数据添加到倒排索引中,添加的数据称为文档。所以要进行ES的操作要先创建索引,再添加文档,这样才能进行后续的查询操作。
要操作ES可以通过Rest风格的请求来进行,也就是说发送一个请求就可以执行一个操作。比如新建索引,删除索引这些操作都可以使用发送请求的形式来进行。
创建索引
books是索引名称,下同
PUT请求 http://localhost:9200/books
|
发送请求后,看到如下信息即索引创建成功
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "books"
}
|
重复创建已经存在的索引会出现错误信息,reason属性中描述错误原因
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "resource_already_exists_exception",
"reason": "index [books/VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w] already exists",
"index_uuid": "VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w",
"index": "books"
}
],
"type": "resource_already_exists_exception",
"reason": "index [books/VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w] already exists", # books索引已经存在
"index_uuid": "VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w",
"index": "book"
},
"status": 400
}
|
查询索引
GET请求 http://localhost:9200/books
|
查询索引得到索引相关信息,如下
{
"book": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "books",
"creation_date": "1645768584849",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "VgC_XMVAQmedaiBNSgO2-w",
"version": {
"created": "7160299"
}
}
}
}
}
|
如果查询了不存在的索引,会返回错误信息,例如查询名称为book的索引后信息如下
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [book]",
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
}
],
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [book]", # 没有book索引
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
},
"status": 404
}
|
删除索引
DELETE请求 http://localhost:9200/books
|
删除所有后,给出删除结果
如果重复删除,会给出错误信息,同样在reason属性中描述具体的错误原因
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [books]",
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
}
],
"type": "index_not_found_exception",
"reason": "no such index [books]", # 没有books索引
"resource.type": "index_or_alias",
"resource.id": "book",
"index_uuid": "_na_",
"index": "book"
},
"status": 404
}
|
创建索引并指定分词器
前面创建的索引是未指定分词器的,可以在创建索引时添加请求参数,设置分词器。目前国内较为流行的分词器是IK分词器,使用前先在下对应的分词器,然后使用。IK分词器下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
分词器下载后解压到ES安装目录的plugins目录中即可,安装分词器后需要重新启动ES服务器。使用IK分词器创建索引格式:
PUT请求 http:
请求参数如下(注意是json格式的参数)
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"id":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"name":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"type":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"description":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"copy_to":"all"
},
"all":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
|
创建完毕后返回结果和不使用分词器创建索引的结果是一样的,此时可以通过查看索引信息观察到添加的请求参数mappings已经进入到了索引属性中
{
"books": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": { #mappings属性已经被替换
"properties": {
"all": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"description": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": [
"all"
],
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": [
"all"
],
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"type": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "books",
"creation_date": "1645769809521",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "DohYKvr_SZO4KRGmbZYmTQ",
"version": {
"created": "7160299"
}
}
}
}
}
|
ES文档操作
目前我们已经有了索引了,但是索引中还没有数据,所以要先添加数据,ES中称数据为文档,下面进行文档操作。
添加文档,有三种方式
POST请求 http:
POST请求 http:
POST请求 http:
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{
"name": "springboot",
"type": "springboot",
"description": "springboot"
}
|
查询文档
条件查询
删除文档
修改文档(全量更新)注意参数要写全,不然会丢失数据
PUT请求 http:
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{
"name": "springboot",
"type": "springboot",
"description": "springboot"
}
|
修改文档(部分更新)有就更新,没有就创建
POST请求 http:
文档通过请求参数传递,数据格式json
{
"doc":{
"name":"springboot"
}
}
|
SpringBoot整合ES客户端操作
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
spring:
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200
|
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate template;
}
|
SpringBoot平台并没有跟随ES的更新速度进行同步更新
ES提供了High Level Client操作ES
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
client.close();
}
}
|
配置ES服务器地址与端口9200,记得客户端使用完毕需要手工关闭。由于当前客户端是手工维护的,因此不能通过自动装配的形式加载对象。
高级别客户端操作是通过发送请求的方式完成所有操作的,ES针对各种不同的操作,设定了各式各样的请求对象,上例中创建索引的对象是CreateIndexRequest,其他操作也会有自己专用的Request对象。
将上述代码格式转换成使用测试类的初始化方法和销毁方法进行客户端对象的维护。
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot18EsApplicationTests {
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}
|
添加文档
创建索引(IK分词器):
@Test
void testCreateIndexByIk() throws IOException {
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
String json = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"type\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"description\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
|
IK分词器是通过请求参数的形式进行设置的,设置请求参数使用request对象中的source方法进行设置,至于参数是什么,取决于你的操作种类。当请求中需要参数时,均可使用当前形式进行参数设置。
添加文档:
@Test
void testCreateDoc() throws IOException {
Book book = bookDao.selectById(1);
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.index(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
|
添加文档使用的请求对象是IndexRequest,与创建索引使用的请求对象不同。
批量添加文档:
@Test
void testCreateDocAll() throws IOException {
List<Book> bookList = bookDao.selectList(null);
BulkRequest bulk = new BulkRequest();
for (Book book : bookList) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
bulk.add(request);
}
client.bulk(bulk,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
|
批量做时,先创建一个BulkRequest的对象,可以将该对象理解为是一个保存request对象的容器,将所有的请求都初始化好后,添加到BulkRequest对象中,再使用BulkRequest对象的bulk方法,一次性执行完毕。
查询文档
按id查询文档:
@Test
void testGet() throws IOException {
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("books","1");
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
System.out.println(json);
}
|
根据id查询文档使用的请求对象是GetRequest。
按条件查询文档:
@Test
void testSearch() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("books");
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
builder.query(QueryBuilders.termQuery("all","spring"));
request.source(builder);
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
String source = hit.getSourceAsString();
Book book = JSON.parseObject(source, Book.class);
System.out.println(book);
}
}
|
按条件查询文档使用的请求对象是SearchRequest,查询时调用SearchRequest对象的termQuery方法,需要给出查询属性名,此处支持使用合并字段,也就是前面定义索引属性时添加的all属性。
修改文档
@Test
void testUpdate() throws IOException {
Book book = new Book();
book.setId(15);
book.setName("测试数据123张三");
book.setType("测试数据123");
book.setDescription("测试数据123");
bookDao.updateById(book);
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("books", book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
updateRequest.doc(json, XContentType.JSON);
client.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
|
删除文档
@Test
void testDelete() throws IOException {
DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("books", "18");
client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
|
Mapping
mapping常见属性
type
字符串text、keyword
数字long、integer、short、byte、double、float
布尔boolean
日期date
对象object
index
analyzer
properties
Index
DSL
- 创建索引库:PUT /索引库名
- 添加字段:PUT /索引库名/_mapping
- 删除索引库:DELETE /索引库名
- 查询索引库:GET /索引库名
JAVA
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是Create、Get、Delete
- 准备DSL( Create时需要,其它是无参)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
Document
DSL
- 创建文档:POST /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 查询文档:GET /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 删除文档:DELETE /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id
- 修改文档:
- 全量修改:PUT /{索引库名}/_doc/文档id { json文档 }
- 增量修改:POST /{索引库名}/_update/文档id { “doc”: {字段}}
JAVA
- 初始化RestHighLevelClient
- 创建XxxRequest。XXX是Index、Get、Update、Delete、Bulk
- 准备参数(Index、Update、Bulk时需要)
- 发送请求。调用RestHighLevelClient#.xxx()方法,xxx是index、get、update、delete、bulk
- 解析结果(Get时需要)
ik_smart/ik_max_word

